Introduction
In today's globe, emergency situations can strike at any moment, and being prepared is necessary. One of the key abilities that can save lives is cardiopulmonary resuscitation (MOUTH-TO-MOUTH RESUSCITATION). Teens stand for a critical populace that can be educated to react properly in emergency situations. By equipping them with CPR training, we not just encourage them with life-saving abilities but additionally promote a society of readiness and responsibility. This article explores the value of CPR training for teenagers, what to anticipate in first aid courses, and how these skills contribute to their personal growth and area safety.
Understanding mouth-to-mouth resuscitation Educating for Teens: Preparing the Next Generation for Emergencies
What is CPR?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (MOUTH-TO-MOUTH RESUSCITATION) is a lifesaving technique made use of during emergencies when somebody's heart beat or breathing has actually quit. It consists of upper body compressions and rescue breaths that aid maintain blood circulation to important body organs till professional clinical assistance arrives. Comprehending the basics of CPR is essential for teens who might discover themselves in emergency situation situations.
Why Do Teens Required Mouth-to-mouth Resuscitation Training?
Teens are typically at celebrations, sports occasions, or even home events where emergencies might take place. By learning mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, they become proactive members of their neighborhood that can act emphatically throughout situations. The capacity to carry out mouth-to-mouth resuscitation confidently can transform a potentially awful scenario into one where lives are saved.
Benefits of Emergency treatment Courses for Teens
First aid programs do greater than simply teach participants exactly how to provide immediate care; they infuse confidence and reinforce analytic skills. For teenagers, this experience can build character and urge leadership qualities.
- Empowerment: Understanding of first aid and CPR empowers young people. Confidence Building: Successfully finishing a training course gives teenagers with a sense of achievement. Community Solution: Educated teens can volunteer in different setups such as schools or sporting activities teams.
The Framework of mouth-to-mouth resuscitation Courses for Teens
Course Period and Format
Most emergency treatment training courses are created to fit within a couple of hours to a couple of days, relying on the deepness of training provided. Normally, a standard emergency treatment course will certainly cover:
- Theory: The concepts behind emergency treatment techniques. Practical Abilities: Hands-on practice with mannequins or through simulations.
Key Components Covered in Emergency Treatment Courses
Understanding Emergency situation Situations- Recognizing when to require help Assessing the scene for safety
- Performing high-quality upper body compressions Providing rescue breaths correctly
- Learning how to operate an AED Importance of early defibrillation
- Techniques for adults, children, and infants Recognizing indicators of respiratory tract obstruction
- Cuts and scrapes Sprains and fractures
The Value of Accreditation in First Aid Training
Obtaining Your Emergency treatment Certificate
Completing an emergency treatment course generally finishes in getting a certification that validates your skills. This certification offers multiple functions:
- It demonstrates proficiency in emergency situation response. Many companies require accreditation for engagement in specific events.
Keeping Qualifications Current
Just like any kind of life skill, it's important to maintain your understanding up-to-date. Most companies recommend renewing certifications every two years.
How Young adults Can Get Involved with Emergency Treatment Training
Finding Neighborhood First Aid Courses
Teenagers curious about getting their emergency treatment certificate should check out local community centers, institutions, or health and wellness companies that provide certified programs.
Helpful Resources:
- American Red Cross St John Ambulance Local medical facilities or wellness departments
Online vs In-Person Training Options
With developments in technology, on the internet components have actually come to be prominent yet might lack hands-on practice essential for genuinely mastering strategies. A mixed technique-- incorporating on-line concept with functional sessions-- could be most beneficial.
Creating Recognition Among Peers about CPR Training for Teenagers: Preparing the Future Generation for Emergencies
Peer Education Initiatives
Encouraging teenagers to share what they have actually discovered with their pals can magnify the influence of training programs:

- Forming study groups focused on emergency situation preparedness. Hosting workshops at schools or community centers.
Using Social Media as a Platform
Teens today are heavily engaged on social media sites platforms; making use of these channels can assist spread out understanding about the value of emergency treatment training among peers.
Real-Life Stories That Emphasize the Significance of CPR Educating for Teens
Case Research study 1: Saving a Life at Institution Sports Event
A young adult learnt CPR was able to conserve their buddy's life throughout a football match when he fell down on the area as a result of heart attack. Their quick thinking permitted them to carry out proper breast compressions up until emergency solutions arrived.
Case Study 2: Household Emergency at Home
Another example entailed brother or sisters who had actually taken a first aid course with each other. When their more youthful bro unintentionally choked on food during supper, they immediately understood what steps to take due to the fact that they remembered their training-- leading them successfully via the emergency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Teen Mouth-to-mouth Resuscitation Training
1. What age must teens start taking mouth-to-mouth resuscitation courses?
A lot of companies recommend beginning as early as 12 years of ages; however, younger kids can likewise learn standard concepts with appropriate programs customized to their age group.

2. How much time does it require to finish an emergency treatment course?
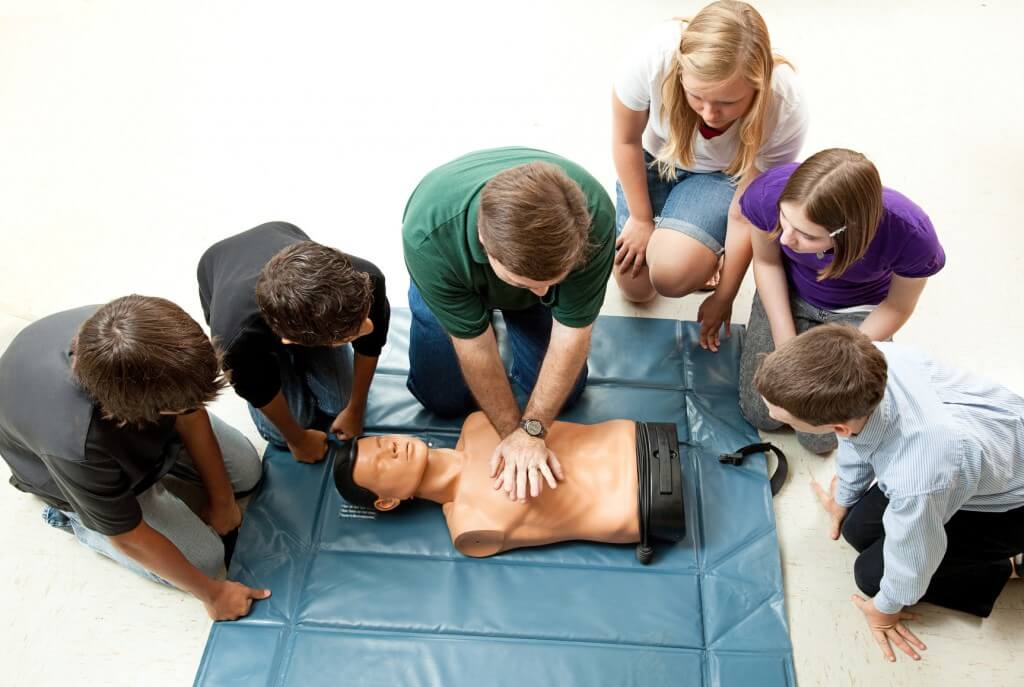
Courses usually vary from 4 hours as much as 16 hours relying on material depth-- the average being around 8 hours.
3. Exist any type of prerequisites prior to enrolling?
No formal requirements exist; nonetheless, it's practical if individuals have an understanding of basic clinical terms.
4. Will I obtain qualification after completing my course?
Yes! Upon effective completion and passing any needed analyses you'll receive an official emergency treatment certificate legitimate for two years.
5. Can I take these programs online?
Lots of establishments use hybrid formats combining on the internet concept with called for functional sessions kept in individual-- this is suggested by market standards.
6. Is it necessary to renew my accreditation periodically?
Yes! Normal recertification guarantees your skills remain skilled and updated according to current guidelines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, equipping teens with knowledge regarding cardiopulmonary resuscitation (MOUTH-TO-MOUTH RESUSCITATION) through specialized training programs is indispensable not just for their growth but likewise improves community security generally. With reliable training sources offered-- from neighborhood training courses offering thorough guideline on both basic emergency treatment methods in addition to sophisticated life assistance methods-- it's less complicated than in the past for young people anxious about making an impactful difference throughout emergencies!
As we move forward right into an unforeseeable world full of challenges requiring swift action-- allow us spend our efforts in the direction of enlightening this future generation so they're prepared not simply academically yet likewise almost geared up when Go here dealt with against real-life scenarios demanding immediate responses like those calling for prompt interventions such as performing efficient cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).